2025’s Most Influential Customer Leaders Powering Business Transformation
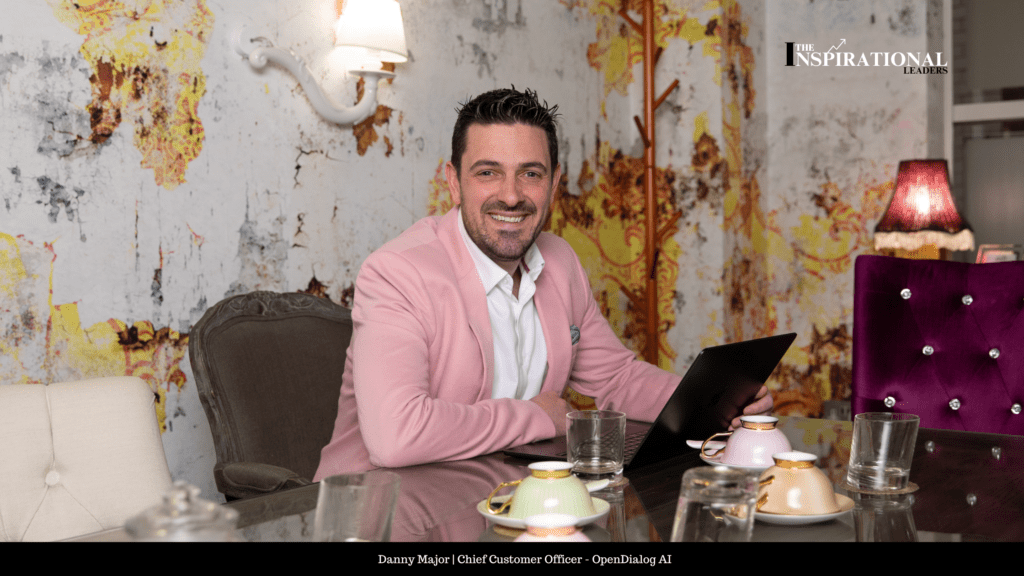
Digital Version In a business world increasingly shaped by rapid digital innovation, the role of customer leaders has transformed dramatically. Danny Major, serving as the Chief Customer Officer at OpenDialog AI, is leading this transformation. His approach goes far beyond traditional service delivery—he views customer leadership as a strategic enabler of both client and business success. For Danny, technology is simply a tool to achieve his goals. At OpenDialog AI, his core mission is to align cutting-edge conversational AI tools with tangible, measurable business outcomes. He places strong emphasis on helping clients navigate the complexities of an ever-evolving tech landscape while keeping their end goals front and center. This vision is not confined to his role alone—Danny fosters a company-wide culture of consultative, impact-driven thinking. His team is encouraged to see every interaction through the customer’s lens and to continuously explore how innovation can translate into real, sustainable transformation. customer leadership isn’t about overseeing interactions – it’s about unlocking potential at every touchpoint. In this AI-powered era, our mission is to humanize technology, build trust through intelligent dialogue, and turn every challenge into a growth story worth telling. Guiding Principles Behind Exceptional Customer Experiences At OpenDialog AI, the customer experience strategy is distilled into a powerful framework: “Understand, Educate, Execute, Evolve.” These four pillars serve as the foundation of every customer relationship. The journey begins with a deep understanding of each client’s strategic objectives, followed by a commitment to education. Especially in regulated sectors, helping clients gain clarity and confidence about AI adoption is crucial. Execution is the next step—tailored, outcome-driven deployments that fit the unique challenges of each organization. Finally, OpenDialog AI supports an evolutionary process, helping customers grow with the technology and continuously improve as their needs shift. This principle-based approach is deeply intertwined with the company’s mission: enabling businesses in complex, regulated industries to safely and confidently harness the potential of Generative AI. By aligning each project with the broader mission, OpenDialog creates not just solutions, but trusted partnerships. When Customer Insight Shapes Innovation Danny Major believes that the best innovations emerge directly from customer insight. A clear example of this was the development of the company’s Co-Pilot solution. Many clients were eager to implement AI, but hesitant to hand over full control to automated systems. In response, OpenDialog created a hybrid model, where AI works in tandem with human agents. By using this approach, clients could safely experiment with AI applications. It delivered faster call resolutions and higher accuracy, all while easing the path to digital transformation. Most importantly, it demonstrated how customer feedback could become the engine behind meaningful product development. In an era shaped by algorithms and automation, true leadership is measured by how deeply we understand people not just processes and how boldly we turn technology into trust. Driving Impact Through Conversational AI OpenDialog AI’s conversational agents are not simply tools—they are designed to become integral members of customer-facing teams. Capable of managing entire customer journeys, these agents bring personalization and contextual relevance to each interaction. This is especially critical in sectors where accuracy, clarity, and compliance are non-negotiable. Through these agents, businesses can not only reduce operational costs and compliance risks, but also boost satisfaction and engagement. From quoting to claims, OpenDialog’s AI ensures each interaction feels human, responsive, and aligned with the customer’s intent. This capability extends across industries, positioning OpenDialog’s platform as a versatile, future-ready solution for customer engagement. Measuring What Truly Matters Rather than relying solely on traditional KPIs, Danny takes a tailored approach to measuring customer success. While metrics like product utilization provide some insight, he places higher value on understanding what success looks like for each individual client. Reduced call handling time, improved customer experience scores, enhanced compliance—each of these could be a core outcome depending on the client’s priorities. This customized methodology ensures that every success strategy is rooted in what matters most to the customer. Danny and his team actively listen, ask the right questions, and design engagement strategies that reflect real-world impact. This personalized view of success makes the partnership stronger and the outcomes more meaningful. Keeping Humanity at the Center of Innovation With the rise of generative AI and automation, maintaining a human touch is more important than ever. Danny emphasizes that OpenDialog AI sees its agents not as replacements, but as collaborators. He often describes them as “silicon-based colleagues” who support the human workforce. In every implementation, Danny’s team works closely with clients to ensure their employees are prepared to manage and guide the AI systems. This human-in-the-loop model builds trust and empowers clients to take ownership of their AI journey. Co-creation, ethical oversight, and skill development are central to this strategy. By keeping humanity at the heart of innovation, OpenDialog helps clients move forward with confidence and care. Creating Unity Across Departments Cross-functional collaboration is key to customer success. At OpenDialog AI, Danny encourages what he calls the “empty chair” mindset. Every team is urged to consider the customer’s perspective in decision-making, as if the customer were present in the room. Customer insights are shared widely across departments, and clients are frequently invited to company meetings to share their stories firsthand. Such interactions enhance empathy and insight, helping sales, engineering, and product teams stay connected to real-world conditions. Additionally, structured feedback mechanisms ensure customer teams have a voice in product development and strategic planning. This open dialogue is instrumental in building a company culture where everyone is invested in customer success. Overcoming the Challenge of Scaling Personalization Scaling personalized experiences globally is no easy task. Danny identifies two main pitfalls: over-engineering from the start and relying too heavily on external advice. OpenDialog promotes an iterative, test-and-learn strategy that focuses on gradually building success through incremental achievements. By collaborating closely with clients and drawing from their internal expertise, the company develops solutions that are not only personalized but also scalable. This co-created path allows for adaptability, ensuring solutions evolve with changing market and organizational needs. Through this approach, OpenDialog helps clients